Business Analyst Vs Data Analyst – How are they Different from Each Other?
Are you trying to figure out the difference between a business analyst and a data analyst? A lot of people think that both jobs are pretty much same in nature but there are some distinct differences. As businesses become more driven by technology, the roles of these two positions have grown in importance.
With so much at stake, uncovering all the information available can give businesses an edge over competitors – which is why having knowledgeable pros on your team is essential for success.
In this blog post, we will explore how these paths differ and highlight how each role contributes to improving corporate performance.
Business Analytics and Data Analytics
First things first. Let’s see what these terms actually mean – Business Analytics and Data Analytics. Read on.
As business and data analytics, both involve working with large sets of raw data, it can be difficult to discern the essential distinctions between them. To better understand, let’s explore how each specializes in leveraging unique insights from mountains of data – ultimately helping organizations make sound decisions that drive improved performance.
| Business analytics | Data analytics |
|---|---|
| Business analytics is an invaluable skill that can help guide companies to success. By understanding and analyzing raw data, organizations have the insights they need to make strategic decisions such as whether a new product line should be developed or which project has higher priority. With the right combination of skills, tools, and applications business analytics provide powerful guidance for core functions like marketing, customer service, and sales into optimized effectiveness resulting in increased efficiency overall. | By leveraging today's technology, data analytics makes it possible to unveil never-before-seen patterns in vast datasets and utilize this information to make informed decisions. Looking beyond surface-level observations, organizations can now uncover insights on topics such as how geography influences customer preferences or the likelihood of a customer defecting. By harnessing their internal data through various methods -data science, mining models, etc.- companies are better equipped than ever before to transform raw figures into significant results that drive business success. |
Business Analyst Vs Data Analyst
Business and data analysts both analyze information to help businesses make better decisions – but their approaches are distinct. Business Analysts focus on understanding the company’s processes/business applications, while Data Analysts tackle complex questions using quantitative methods. Both teams play essential roles in ensuring a successful business strategy!
Let’s analyze these roles one by one.
What Is The Role Of A Business Analyst?
Business analysts are the gatekeepers of organizational success, working to ensure an efficient and optimized environment. They conduct comprehensive evaluations of operational systems and processes, along with interviews with staff members in order to pinpoint areas needing improvement.
Once their findings have been presented to management and stakeholders alike, they demonstrate how solutions can be implemented through either IT or non-IT means.
What Is The Role Of A Data Analyst?
Data analysts play a critical role in facilitating well-informed decision-making. By analyzing and visualizing data, they can uncover powerful insights that allow business leaders to identify opportunities for growth or areas of improvement.
Data analysts are experts at connecting the dots between raw information sources and presenting a story through their presentations – giving stakeholders clear direction on which path forward is most suitable. Common responsibilities range from collaborating with executives to define issues, acquiring pertinent data sets, cleansing datasets before analysis; discovering trends within data sets; displaying results clearly with visuals; culminating investigation findings into succinct reports or stories.
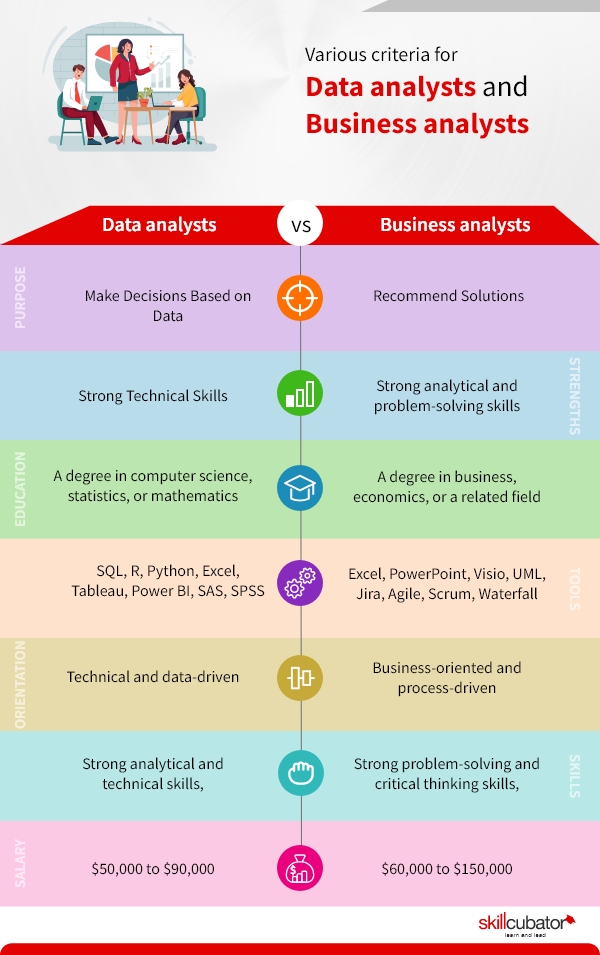
Let’s have a comparative analysis of various criteria for data analysts and business analysts.
| Criteria | Data Analysts | Business Analysts |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | To collect, process, and analyze data to help make decisions based on data | To identify business needs and opportunities, and to recommend solutions |
| Skills | Strong technical skills, including proficiency in data manipulation and analysis tools | Strong analytical and problem-solving skills, as well as excellent communication and business acumen |
| Education | A degree in a related field such as computer science, statistics, or mathematics is common | A degree in business, economics, or a related field is common |
| Responsibilities | Collecting and analyzing data from various sources, creating reports and visualizations, identifying patterns and trends, and making recommendations based on findings | Identifying business needs and opportunities, gathering and analyzing data, creating reports and presentations, and making recommendations for improvements |
| Process | Collect and clean data, perform exploratory data analysis, build models and create visualizations, communicate findings and make recommendations | Identify business needs and opportunities, gather and analyze data, create process flows and diagrams, create reports and presentations, communicate findings and make recommendations |
| Tools | SQL, R, Python, Excel, Tableau, Power BI, SAS, SPSS | Excel, PowerPoint, Visio, UML, Jira, Agile, Scrum, Waterfall |
| Output | Reports, visualizations, dashboards, statistical models, predictive models, data products | Business requirements documents, process flows, diagrams, project plans, presentations, recommendations for improvements |
| Orientation | Technical and data-driven | Business-oriented and process-driven |
| Strengths | Strong analytical and technical skills, ability to work with large amounts of data, attention to detail | Strong problem-solving and critical thinking skills, ability to understand and analyze business processes, excellent communication and presentation skills |
| Salary | The median salary for a data analyst is around $65,000 per year in the United States. However, it can range from $50,000 to $90,000 depending on the level of experience and location. | The median salary for a business analyst is around $75,000 per year in the United States. However, it can range from $60,000 to $150,000 depending on the level of experience and location. |
| Career path | Many data analysts start as data entry or data analysis assistants and then work their way up to become data analysts. Some data analysts also become data scientists or data engineers. | Business analysts often start in entry-level roles such as business analyst associates or junior business analysts and then progress to become senior business analysts or business analyst managers. Some business analysts also become management consultants or project managers. |
Note: These are not hard and fast rules, and there may be some overlap between the roles depending on the organization and the specific job.
Business Analyst And Data Analyst — How to Choose a Career Path?
Choosing between a career as a data analyst and a business analyst can be challenging. These two roles have some similarities but also significant differences. Here are a few factors to consider when making your decision.
Read on about how you can decide based on certain attributes!
Skills and interests: Consider your current skills and interests, as well as the skills and interests that you would like to develop. Data analysts often have strong technical skills and a passion for working with data, while business analysts have a passion for understanding and improving business processes.
Career goals: Think about what you want to achieve in your career. Data analysts often focus on using data to make informed decisions, while business analysts focus on identifying and solving business problems.
Work environment: Consider the type of work environment that you prefer. Data analysts often work in technical or research-oriented environments, while business analysts often work in corporate or consulting environments.
Education: Think about the educational background that you have or would like to have. Data analysts typically have a background in computer science, statistics, mathematics, or engineering, while business analysts often have a background in business or a related field such as economics, management, or finance.
Ultimately, it’s important to research the different roles and gain a deeper understanding of the day-to-day responsibilities, and industry trends. That will help you to make a more informed decision about which path is the best fit for your skills, interests, and goals.
How Skillcubator Can Help You Progress In Your Career?
| According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the employment of business analysts is projected to grow 11% from 2019 to 2029, much faster than the average for all occupations. Business analyst role is listed as one of the top jobs in the US by the BLS According to the Project Management Institute (PMI), business analysts are the most in-demand project management role. |
| According to the Project Management Institute (PMI), data analysts are the second most in-demand project management role. According to LinkedIn, Data Analyst is the third most sought-after skill among employers globally. According to a report by IBM, the demand for data analysts is expected to increase by 28% by 2020. |
With both data science and engineering receiving interest from companies around the world, getting ready for your future career has never been more important.
At Skillcubator, we provide comprehensive career-building training courses and certifications for aspiring business analysts and data analysts. With our unique program structure backed by expertise in the industry, you can be sure that your transition into a higher level of success will leave you more than prepared!
Gain valuable skills and knowledge to change your career trajectory with our Business Analysis or Data Analyst courses. Start charting a path forward toward success today!
Courses we offer:
Certified Agile Business Analysis with PSM-I and PSPO-I Certifications
Robotics Process Automation (RPA) Business Analysis
Data Analysis and Data Analytics
In A Nutshell
Hope you had a detailed read. Becoming a Business Analyst or Data Analyst can open the door to many career opportunities. Either way, both roles are important in an organization. The main difference between being, business analysts focus on understanding and improving business processes while data analysts focus on analyzing data to support decision-making.
If you’re interested in pursuing a career in either field, we offer several courses that can help you get started. Visit our courses page to view course options or contact us via our contact page if you have any questions.
We’d be happy to help you choose the right course for your needs and goals.
